A gate valve is a linear motion valve used to start or stop
fluid flow. The name gate is derived from the appearance of the disk in the flow stream.
 |
| Gate valve Diagram |
The disk of a gate valve is completely removed from the flow stream when the
valve is fully open.When the
valve is fully closed, a disk-to-seal ring contact surface exists for
360 degree.With the proper mating of a disk to the seal ring, very little or no leakage occurs across the disk when the gate valve is closed.
A gate valve can be used for a wide variety of fluids and provides a tight seal when closed.
Major disadvantages of a gate valve
- It is not suitable for throttling applications.
- It is prone to vibration in the partially open state.
- It is more subject to seat and disk wear than a globe valve.
- Repairs, such as lapping and grinding, are generally more difficult to accomplish.
Gate valves are available with a variety of disks. Classification of gate valves is usually made by the type disk used:
Solid wedges, flexible wedges, and split wedges are used in valves having inclined seats. Parallel disks are used in valves having parallel seats.
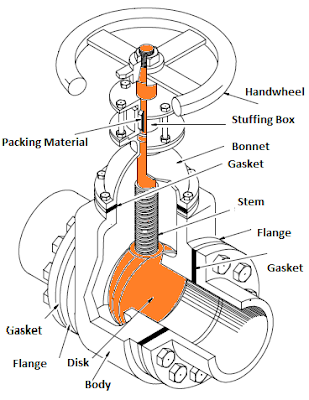 |
| Gate valve |
Regardless of the style of wedge or disk used, the disk is usually replaceable. In services where solids or high velocity may cause rapid erosion of the seat or disk, these components should have a high surface hardness and should have replacement seats as well as disks. If the seats are not replaceable, seat damage requires removal of the valve from the line for refacing of the seat, or refacing of the seat in place. Valves being used in corrosion service should normally be specified with replaceable seats.
Gate Valve Stem Design
Gate valves are classified as either rising stem or non rising stem valves. For the non rising stem gate valve, the stem is threaded on the lower end into the gate. As the hand wheel on the stem is rotated, the gate travels up or down the stem on the threads while the stem remains vertically stationary. This type of valve will almost always have a pointer-type indicator threaded onto the upper end of the stem to indicate valve position.
The non rising stem configuration places the stem threads within the boundary established by the valve packing out of contact with the environment. This configuration assures that the stem merely rotates in the packing without much danger of carrying dirt into the packing from outside to inside.
Rising stem gate valves are designed so that the stem is raised out of the flow path when the valve is open. Rising stem gate valves come in two basic designs. Some valves have a stem that rises through the hand wheel while others have a stem that is threaded to the bonnet.
Gate Valve Seat Design
Seats for gate valves are either provided integral with the valve body or in a seat ring type of construction. Seat ring construction provides seats which are either threaded into position or are pressed into position and seal welded to the valve body. The latter form of construction is recommended for higher temperature service.
Integral seats provide a seat of the same material of construction as the valve body while the pressed-in or threaded-in seats permit variation. Rings with hard facings may be supplied for the application where they are required.
Small, forged steel, gate valves may have hard faced seats pressed into the body.In some series, this type of valve in sizes from 1/2 to 2 inches is rated for 2500 psig steam service. In large gate valves, disks are often of the solid wedge type with seat rings threaded in, welded in, or pressed in. Screwed in seat rings are considered replaceable since they may be removed and replaced.
I'm really happy reading this blog, it is well explained. Do you know how many gate valves we should used ?
ReplyDelete