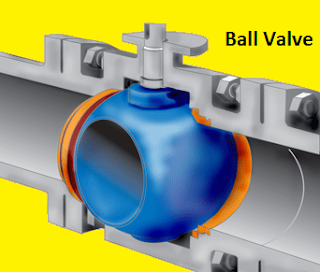
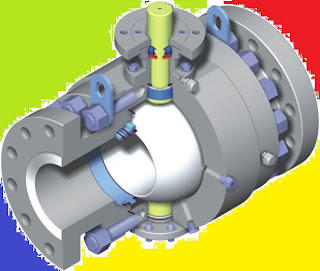
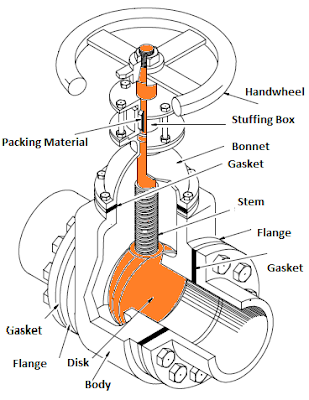
HVAC Valves are such components without which we cannot control flow in pipes .Valves are needed for every media whether it is water, gas, air or any other liquid. Valves would have been needed for solids if they could have ability to flow. Like other areas, valves find its extensive use in HVAC (heating, ventilation and air-conditioning).
With special focus on HVAC, following are the some major hvac application of valves.
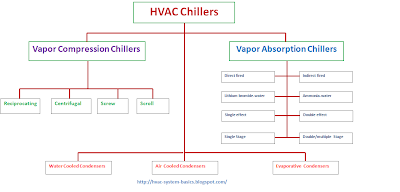
- Water Chiller, the heart of HVAC system, has valves on inlet and outlet lines of chilled water and cooling water. These valves are usually gate and globe valves which are used for isolation and throttling purposes. Water chiller operates on vapor compression cycle or vapor absorption cycles which also require valves internally as a requirement of thermodynamics. For example Refrigerant expansion valve is needed inside a water chiller cycle. Chilled and cooling water headers also need valves for isolation and heating/cooling changeover.
- Similar to water chillers, HVAC hot water generator has also valves on its inlet and outlet for isolation and flow control purposes. If water chiller can also act as water heater then there is no need of hot water generator obviously.
- Chilled water pumps and cooling water pumps have also isolation and throttling valves on their inlets and outlets. When we talk about water pumps then there are also check valves at the outlet of pumps to prevent reverse flow.
- Cooling towers are another hvac equipments which require valves at inlet and outlet for flow control of cooling water. Sometimes a float valve is also in the basin of cooling tower to control the level of water in cooling streams. Valves would also be needed for make-up water lines in HVAC system and cooling towers.
- Air handling units (AHUs) also need valves at inlet and outlet to regulate chilled water as per demand of cooling in the spaces depending upon the type of HVACcontrol system. These air handling unit valves are also connected to some HVAC software to remotely operate them as per cooling/heating demand from HVAC users. Drain valves are also provisioned inside air handling units.
- If Fan Coil Units (FCUs) are installed in individual rooms then valves will also be installed at entry and exit of these units to have precise control of cooling /heating for occupants of that space.